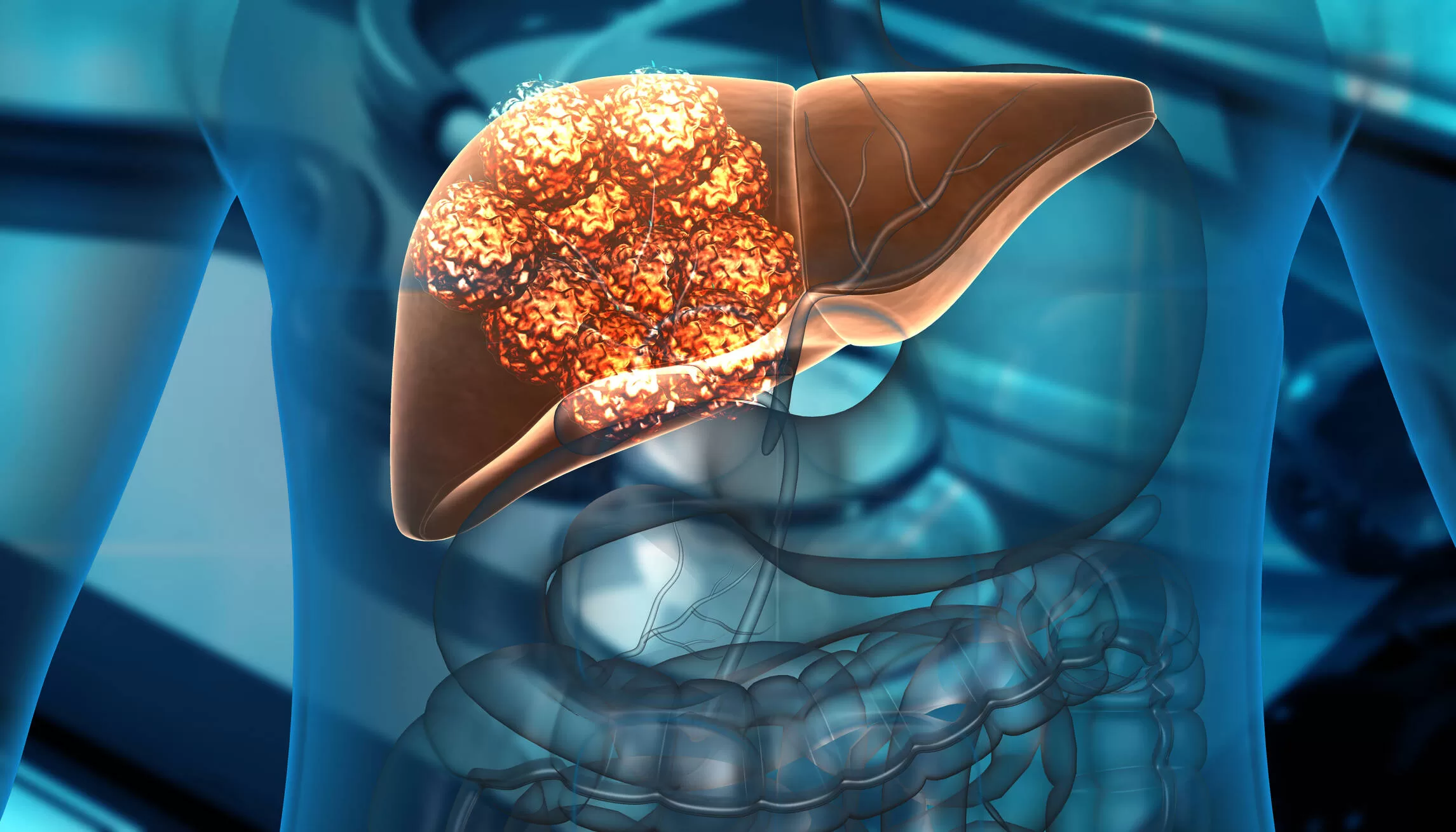
Chronic liver diseases, such as alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis, and cancer, affect more than 1.5 billion people worldwide. In the United States, it is estimated that between 30 and 40% of the population has been diagnosed with NAFLD.
In this case, he adds, “human cells and mouse cells speak different languages, but we have managed to make human liver cells speak their own language inside living mice,” says Richard Flavell, one of the study’s authors.
The team of scientists, led by Eleanna Kaffe, used progenitor stem cells and mature cells known as hepatocytes from a human liver to create a complete liver in a mouse model.
According to the researchers, the humanized liver acquired a tight-fitting shape and performed cellular functions similar to those of a healthy human liver.
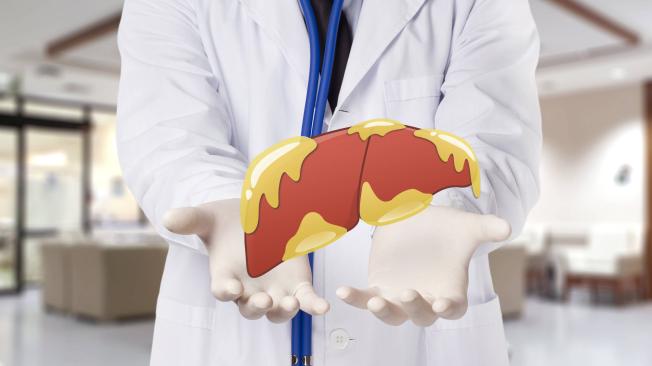
Fatty liver in adults is a disease of metabolic origin that consists of the accumulation of fat in the liver cell.
The researchers found that essential metabolism in the liver is controlled by the activity of endothelial cells, which line the blood vessels that feed the liver.
According to the researchers, the humanized liver model can be immediately used by pharmaceutical companies wishing to assess the safety of experimental drugs designed to treat chronic diseases.
“However, our long-term goal is to find ways to predict, prevent, and treat all liver diseases, which affect people so much,” the authors state.